La automatización está logrando la optimización alimentaria
La automatización es - Una serie sobre los retos y oportunidades de la logística alimentaria.
25 de agosto de 2021
Challenge 4: Food Waste and Safety
Moving from middleman to the last line of defense.
Traditionally, cold storage warehouses have functioned as upstream stops on a long journey ending at grocery and retail stores and ultimately, the consumer. The buffer between production and consumption distributed responsibility of food safety between all parties involved in the product’s journey. The growth of business-to-consumer (B2C) direct delivery companies, however, circumvents traditional supply chain workflows and shifts direct customer contact further upstream. These days, a frontline worker at a warehouse could be the last line of defense for somebody’s dinner.
“Now, what we do impacts somebody at their home. There is no middleman. We have to have the highest level of efficacy and attention to detail because we’re the final quality check.” – Dr. Stephen Neel, Lineage Director of Food Safety
Doing our part to reduce food waste.
There are many factors that can cause food waste – from spoilage and disruptions in temperature regulation to package damage. Even relatively small differences in temperature can mean a big difference in the quality of perishable foods. Maintaining the quality of perishable foods is difficult, especially when multiple players are handling and moving the product. Lack of visibility and human error are the two most common causes of food spoilage during transportation, processing and storage.
According to the Boston Consulting Group (BCG), the amount of food waste created in the supply chain will rise by 1.9% annually from 2015 to 2030. You may think this is a small growth, but when put into perspective, the current 1.6 billion tons wasted every year will increase by 30.4 million tons (Abecasis, Alexander, Meyer zum Felde, Pralle, 2020).
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations reports that nearly $1 trillion of food is lost or wasted every year worldwide. This figure includes food wasted by retail chains or consumers along with food that is lost, damaged or expires as it makes its way through the supply chain. It’s enough food to feed nearly 2 billion people. There are 1 billion undernourished people in the world (UNWFP, 2021). Optimizing the cold chain and dynamic routing can simultaneously decrease waste and undernourishment (Leonard, 2019).
Solution: Optimize food quality and minimize waste with automated, yet agile, workflows.
In the food supply chain, maintaining fundamental compliance through the entire food journey is the primary goal. From there, companies need to decide between merely meeting the minimum standards or going above and beyond, developing best-in-class practices of combining quality and maximization into food safety.
Automation in both decision-making and material handling enables best-in-class practices. Computers can make decisions on the basis of more factors and more information than a human ever could and provide traceability that human decisions cannot. Automated material handling systems put the pallet exactly where the control systems direct it; there is no possibility of a pallet getting lost if it’s been placed by a robot.
Automation removes human error and allows you to focus on optimizing quality. Maximizing quality requires understanding thermodynamics, biology and our customers’ products. Data collection, data analysis and automation ensure that the highest quality of food is available to consumers, while surpassing standard industry guidelines.
Automation in action: Blast freezing line
Blast freezing, the energy-intensive process in which freshly produced perishable goods are safely and rapidly chilled to below-freezing temperatures to retain freshness, is a critical part of the cold chain process. Blast freezing is what makes food frozen prior to storage and shipping.
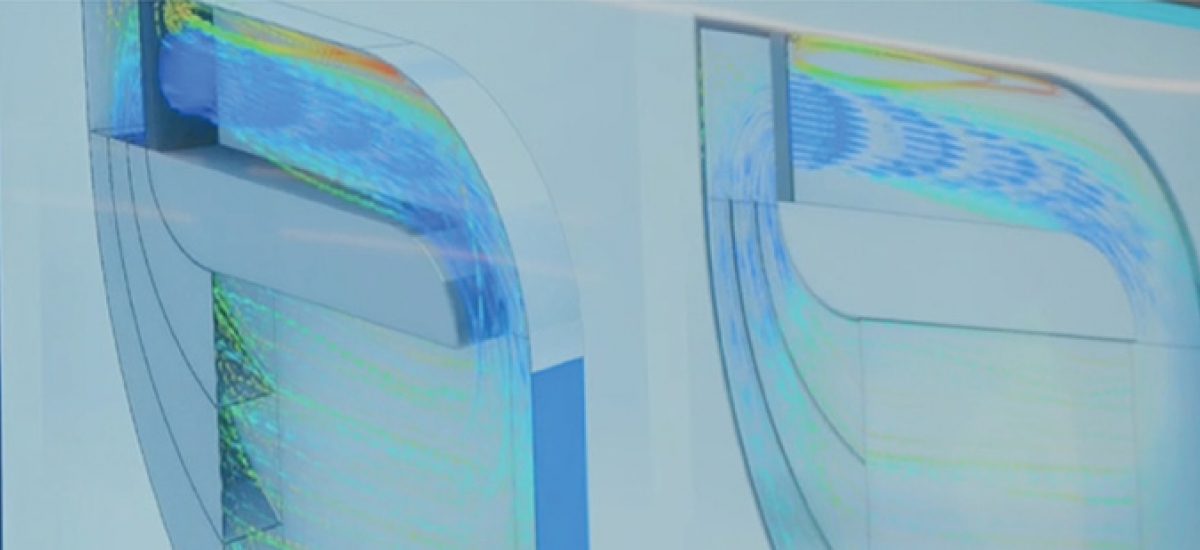
Lineage’s Data Science team has studied and improved the existing blast freezing designs throughout its portfolio. By utilizing techniques, such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and finite element analysis (FEA), we have created and patented new blast freezer designs with improved freezing airflow, which results in higher product freeze quality and enhanced energy efficiency. The newer designs are able to freeze products in as little as half the time of a traditional blast freezer while still being 20% more energy-efficient. Getting perishables to the correct temperature in half the time is just one of the ways that Lineage is maximizing quality.
Lineage’s advancements in blast freezing have not gone unnoticed. We received the Department of Energy’s Better Plants Better Project Award in 2020 as a result of this research and implementation. (In addition to the same awards in 2019 and 2021 for different energy-related innovations.)
Lograr la optimización alimentaria mediante la automatización.
La evolución de la cadena de frío ha aumentado el protagonismo de los trabajadores de almacén, que son la última línea de defensa entre el consumidor y los alimentos potencialmente nocivos. Los cambios en la cadena de suministro de alimentos aumentan lo que está en juego para la cadena de frío, que debe garantizar la seguridad alimentaria y maximizar la calidad.
Debemos elevar los estándares de seguridad alimentaria y, al mismo tiempo, reducir el desperdicio de alimentos. Desde un punto de vista industrial y humanitario, la cantidad de residuos en la cadena de frío afecta negativamente a las economías y comunidades de todo el mundo. Eliminar los residuos en la cadena de frío es un paso esencial hacia un futuro más sostenible.
La automatización es el camino más directo para lograr la seguridad alimentaria y la optimización de los alimentos al tiempo que se reducen los residuos alimentarios. La automatización es esencial, no sólo por la eficiencia que aporta a la industria, sino también para mejorar continuamente la calidad de los alimentos. A medida que aumenta la demanda de los consumidores y se producen cambios que reducen la distancia entre el productor y el consumidor, la automatización de las operaciones de almacén tradicionales es la única respuesta para seguir el ritmo de la demanda con seguridad.
Durante las últimas semanas, hemos tratado numerosos retos a los que se enfrenta la cadena de frío en nuestra serie La automatización es. Tanto si se trata de abordar las preocupaciones por la escasez de mano de obra, el aumento de la demanda de los consumidores, la sostenibilidad o la optimización de los alimentos, está claro que la automatización, la I.A. y la I.O.T. son los métodos más seguros y eficientes para alcanzar los objetivos que compartimos en el sector.
Para una visión práctica de la filosofía de automatización de Lineage, busque nuestra próxima serie de blogs cuando examinemos el lugar de la automatización en la cadena de frío. Exploraremos la flexibilidad de estas nuevas tecnologías y cómo pueden integrarse perfectamente en los flujos de trabajo actuales. También evaluaremos cómo integrar eficazmente el software propietario en todas sus operaciones y qué esperar durante la experiencia. Por último, trataremos las formas de fusionar a los miembros de su equipo con estas nuevas tecnologías.
En última instancia, la automatización en la cadena de frío es fluida. Invertimos continuamente en la mejora de los procesos y, a medida que descubramos formas nuevas y más eficaces de suministrar alimentos al mundo, compartiremos estos avances con usted.
Abecasis, M, Meyer zum Felde, A, y Pralle, A. (2020, 23 de junio). Una receta para reducir la pérdida y el desperdicio de alimentos. Bcg.com. https://www.bcg.com/publications/2020/recipe-to-reduce-food-loss-and-waste.
Leonard, M. (2019, 2 de julio). Informe: Las cadenas de suministro causan el 40% del desperdicio de alimentos en Norteamérica. Supplychaindive.com. https://www.supplychaindive.com/news/developed-countries-food-waste-consumer-level-supply-chain/558023/
(2021, 10 de agosto). 8 Datos que hay que saber sobre el desperdicio de alimentos y el hambre. Wfpusa.org. https://www.wfpusa.org/articles/8-facts-to-know-about-food-waste-and-hunger


